A team from the Technology Engineering of Instrumentation and Control (TEIC) Study Program has recently conducted research that has created new opportunities for ensuring food safety and supporting Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3: Healthy and Prosperous Life.
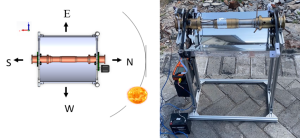
This research focuses on developing a gas sensor array system, also known as an electronic nose (e-nose), for the classification of aromatic rice types. Budi Sumanto, S.Si., M.Eng, a TEIC lecturer, led the research team, with assistance from Salima Nurrahma, a student in the same study program.
“The main objective of this research is to develop an accurate and efficient method for classifying various types of aromatic rice using gas sensor technology and artificial intelligence,” said Budi when interviewed.
Salima added, “By using gas sensor arrays and machine learning algorithms, we can identify the unique characteristics of each type of aromatic rice with a high degree of accuracy.”
This innovation has significant implications for SDG 3, especially in the aspects of food safety and nutrition. The following are some of the anticipated benefits of this research:
- Improving food safety by ensuring aromatic rice’s authenticity and preventing counterfeiting.
- Helping consumers make healthier and more nutritious food choices.
- Support stricter regulations in the food industry, particularly the rice sector.

We hope that the rice processing industry and food regulatory agencies can widely implement this technology. This will contribute to improving people’s quality of life through better food safety assurance,” Budi concluded.
This research is a clear example of how technological innovation can support the achievement of SDGs, especially in ensuring a healthy life and improving people’s welfare.